Vitamin B12 plays important role in the formation of DNA, and it’s essential for the production and maintenance of new cells, including red blood cells and nerve cells.
This vitamin is attached to the food’s proteins, and in order to get released with the help of the hydrochloric acid in the stomach, you need to consume vitamin B12.
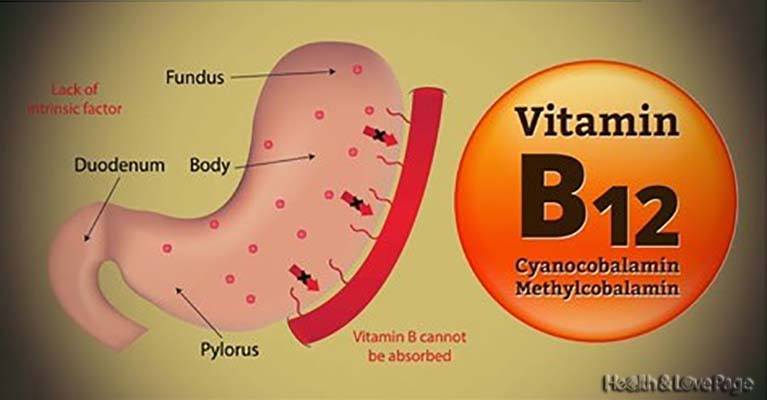 The released B12 combines with the intrinsic factor, a substance which help its absorption in the intestines.
The released B12 combines with the intrinsic factor, a substance which help its absorption in the intestines.
Amount to Consume
The RDA (recommended daily amount) for this vitamin for infants has still not been established because of lack of information.
However, the AI (Adequate Intake) is known, and here are the proper dosages:
- for 0 to 6 months, the AL for both males and females is 0.4 mcg/day;
- for 7 to 12 months, the Al for both males and females is 0.5 mcg/day.
The RDA (Recommended Dietary Allowance) for this vitamin is:
| Age | Males and Females | Pregnancy | Lactation |
| 1 to 3 years | 0.9 mcg | N/A | N/A |
| 4 to 8 years | 1.2 mcg | N/A | N/A |
| 9 to 13 years | 1.8 mcg | N/A | N/A |
| 14 to 19 years | 2.4 mcg | 2.6 mcg | 2.8 mcg |
| 19+ years | 2.4 mcg/day | 2.6 mcg/day | 2.8 mcg/day |
Sources of Vitamin B12
As we’ve mentioned, this vitamin is bound to the proteins in animal foods. However, if you don’t consume proper amount of animal foods, breakfast cereals are great alternative, as they are packed with vitamin B12.
| Food | Amount | Vitamin B12 |
| Top sirloin, beef, lean, broiled, choice | 3 Oz | 2.4 mcg |
| Breakfast cereals, fortified | ¾ cup | 6 mcg |
| Chicken breast, cooked | ½ breast | 0.3 mcg |
| Egg | 1 large | 0.6 mcg |
| Haddock, cooked | 3 Oz | 1.2 mcg |
| Beef liver | 1 slice | 47.9 mcg |
| Milk | 1 cup | 0.9 mcg |
| Clam, mollusks | 3 Oz | 84.1 mcg |
| Sockeye salmon, cooked | 3 Oz | 4.9 mcg |
| Rainbow trout, farmed, cooked | 3 Oz | 4.2 mcg |
| Rainbow trout, wild, cooked | 3 Oz | 5.4 mcg |
| White tuna, canned in water | 3 Oz | 1.0 mcg |
| Plain yogurt, skim milk | 1 cup | 1.4 mcg |
Do You Need to Take Vitamin B12 Supplement?
According to studies, most people in U.S. consume proper amount of this vitamin. However, vitamin B12 supplement is recommended for anyone with intestinal or stomach disorder which impedes the absorption, as well as those who don’t consume meat. Older people with atrophic gastritis might require intake of additional supplements or food sources.
The absorption of vitamin B12 can be affected by some medications, like metformin, H2 receptor antagonists in the treatment of peptic ulcers, and proton pump inhibitors. You can check the levels of this vitamin with a blood test.
What Happens If You Don’t Have Adequate Vitamin B12?
If you have lack of this vitamin, there’s a risk of pernicious anemia. Symptoms of B12 deficiency are weakness, constipation, fatigue, weight loss, loss of appetite, and tingling and numbness in the hands and feet. Further possible signs are confusion, difficulty in maintaining balance, Healthline, dementia, and poor memory. These signs of B12 deficiency can be masked with an excess intake of folate. Therefore, if there’s a concern, and especially if you are on a vegetarian diet, you should check your vitamin B12 levels with blood tests.
Can You Have Too Much Vitamin B12?
So far, vitamin B12 doesn’t have an established Tolerable Upper Limit. But this doesn’t mean that you will gain additional health benefits by consuming excessive amounts of the vitamin. Extremely high levels indicate very low potential for toxicity. The best thing is to stick to the RDA recommendations.
Via Cure Joy
